Like other auxiliary verbs, modal verbs work together with a main verb to give a different meaning to a sentence/clause than if the main verb was used by itself. Modals/ modal verbs/ modal auxiliary verbs are a special type of verbs present in English grammar. These verbs are used irregularly in English grammar.
Uses of modal verbs in English grammar includes providing extra information about the action of the main verb. These auxiliaries express obligation, possibilities, permission or ability in a sentence by adding meaning to the main verb. As per modal verbs rules, the spelling or form do not change, unlike other verbs. Modal verbs help qualify a verb by saying what a person can, may, should, or must do, as well as what might happen. The grammar used with modal verbs can be confusing at times. Generally speaking, modal verbs act like auxiliary verbs in that they are used together with a main verb.
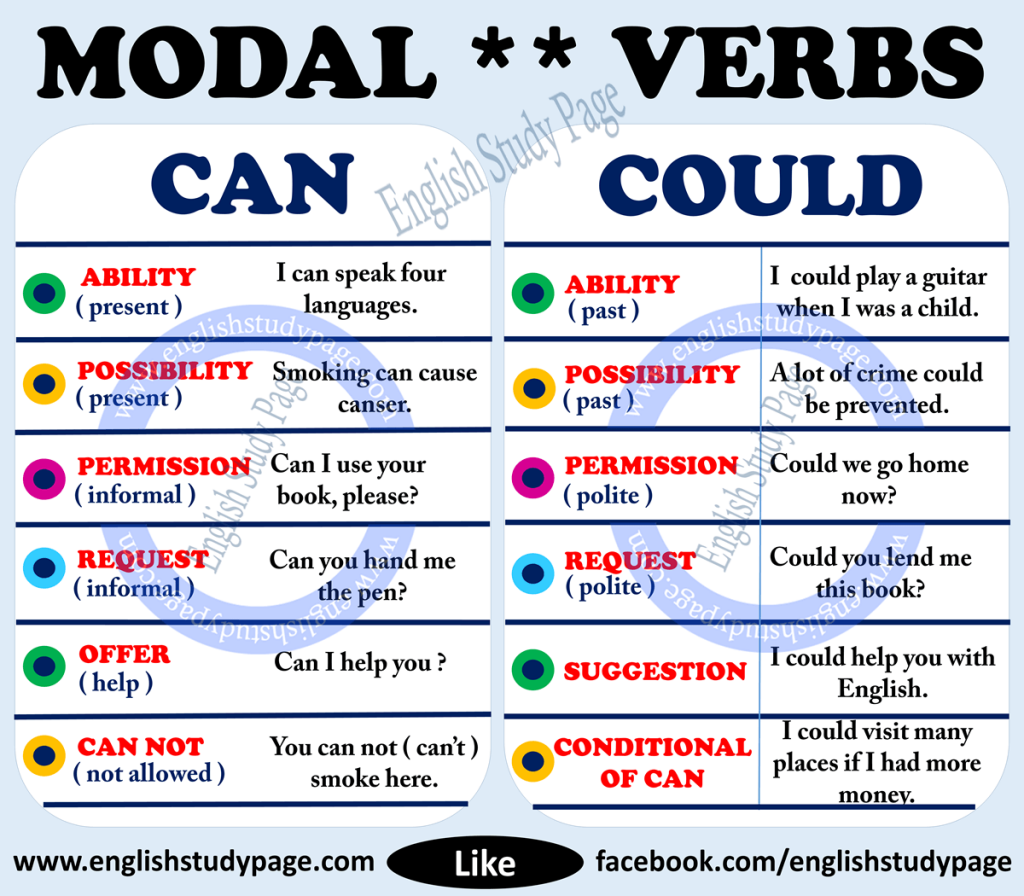
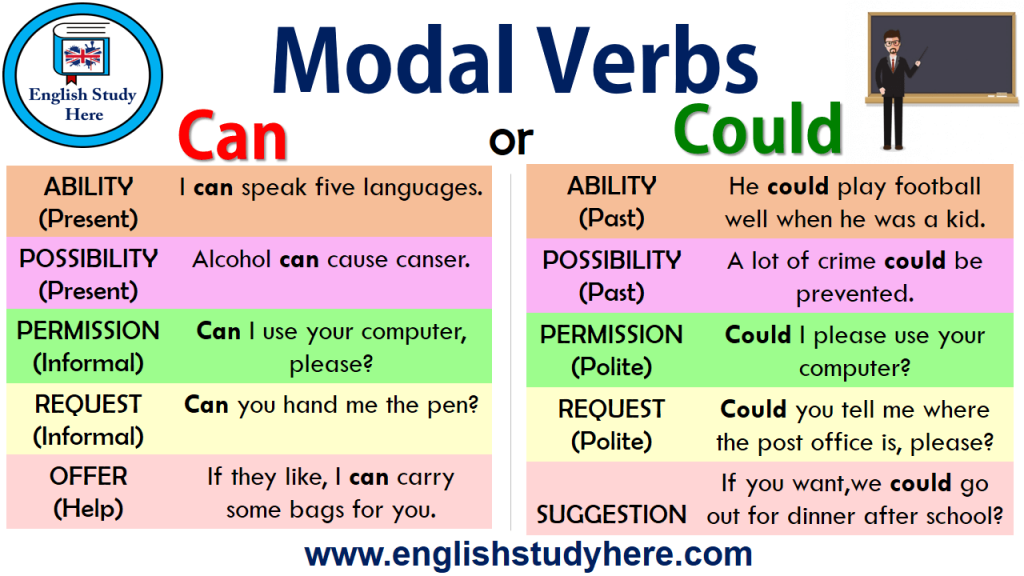
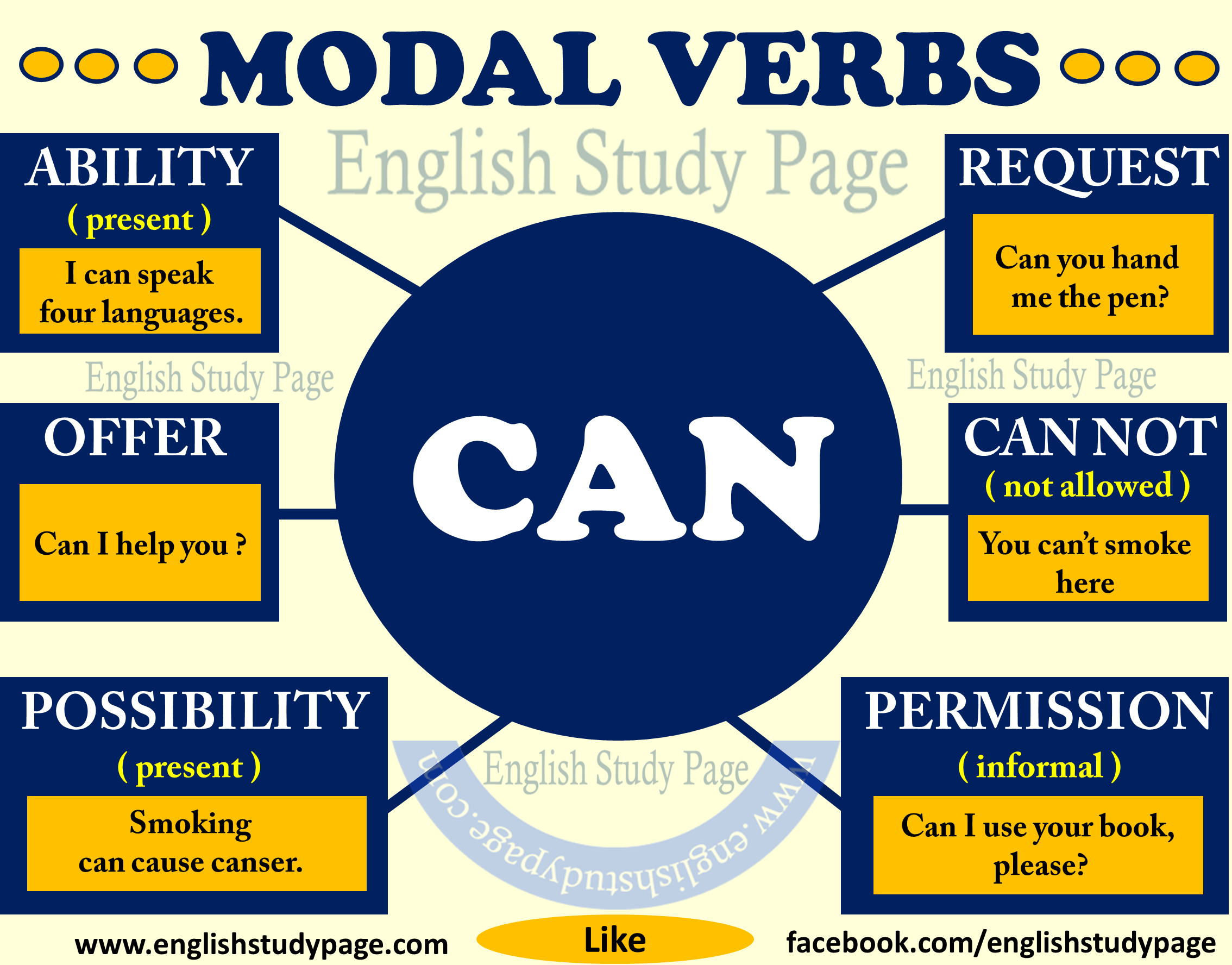
In English, modal verbsare a small class of auxiliary verbs used to express ability, permission, obligation, prohibition, probability, possibility, advice. The modal verbs in English grammar are can, could, may, might, must, need not, shall/will, should/ought to. They express things like ability, permission, possibility, obligation etc. They do not take -s in the simple present and they do not have a past simple or past participle form. However, some modal verbs have alternative forms that allow us to express the same ideas in different tenses.
In the strict sense, though, these other verbs do not qualify as modal verbs in English because they do not allow subject-auxiliary inversion, nor do they allow negation with not. If, however, one defines modal verb entirely in terms of meaning contribution, then these other verbs would also be modals and so the list here would have to be greatly expanded. In English, the modal verbs are used to express ability, possibility, permission or obligation. Each one of the modal verbs can be used to express one or more of these modalities.
They can also be used to form the future tense in English and to make conditional sentences. Let's pretend that you're the English teacher and you have some sentences to correct, where the modal verbs have been used wrongly, used incorrectly. Being the teacher and correcting mistakes is sometimes a good way to check that you know how to do it well. And think about which of the three easy rules for modal verbs is being broken in each of these sentences.
It tells you more - it tells you he has an obligation to go, he should go to school. Again no modal verb 'I sing a song', but with a modal verb 'I could sing a song'. I'm showing you it's a possibility - it may or may not happen, my song. So modal verbs are a way of showing a person's relationship with the verb. Modal verbs are auxiliary verbs, also known as helping verbs.
They work with other verbs to show various conditions, such as possibility or necessity. Modal verbs do not change form based on the verb tense of the sentence; they do not have conjugated forms. There are a wide variety of modal auxiliary and their function.
So, let's waste no more time and begin the learning journey. The nine modal verbs outlined above are different from other verbs in that they never change forms. Even when obeying subject-verb-agreement, these verbs will be identical when used with singular or plural subjects as in Cheetahs can run fast and a cheetah can run fast. In addition to this, these verbs typically are used only with certain verb tenses.
For example, you are likely to hear the sentence It might be cloudy tomorrow but are unlikely to hear the sentence It might will be cloudy tomorrow. Generally speaking, these modal verbs are most often used with verbs in the present tenses . In many Germanic languages, the modal verbs may be used in more functions than in English. In German, for instance, modals can occur as non-finite verbs, which means they can be subordinate to other verbs in verb catenae; they need not appear as the clause root. In Swedish, some modal verbs have infinitive forms.
This for instance enables catenae containing several modal auxiliaries. The modal verbs are underlined in the following table. Remember Rule Number Three - for negative modal verbs, just a simple 'not' between the modal and the main verb - I can not drive a car. This one contracts two ways 'I cannot drive a car' or 'I can't drive a car'.
This podcast will use lots of examples to explain how 3 simple rules will help you use the most common modal verbs correctly. So first of all, just in case you don't know - or you may not know the name - what are modal verbs in English? Well, they're words like 'could', 'can', 'should', 'may', 'might', 'ought', 'would', 'must'. And we use them with another verb - 'I could sing a song', 'You can travel abroad', 'He should go to school', 'She may support that charity'. So we use these little modal verbs to give more information about the person's relationship with the action, with the main verb.
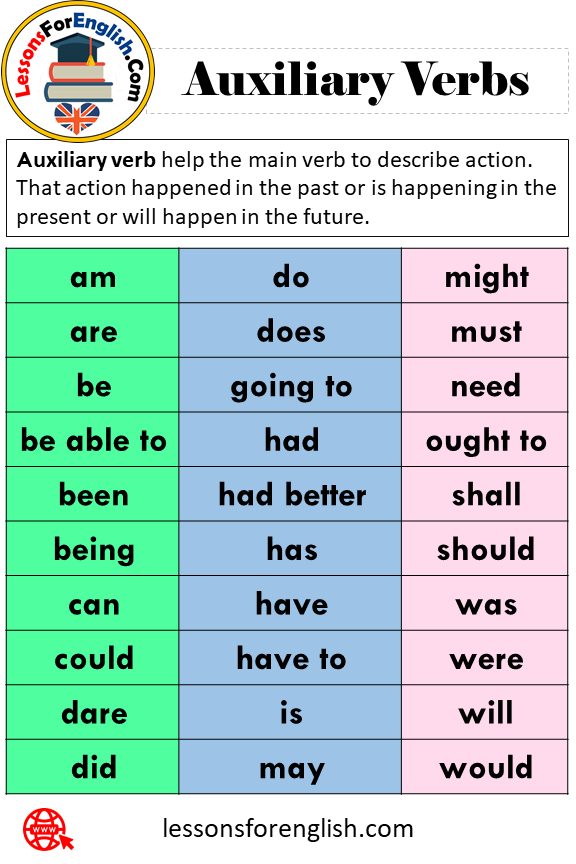
Note - The modal auxiliary verbs are always followed by the base form of the main verb. All the auxiliary verbs except be, do and have are called modals. Unlike other auxiliary verbs modals only exist in their helping form; they cannot act alone as the main verb in a sentence.
Modal verbs, sometimes calledmodals, are auxiliary verbs . They express such things as possibility, probability, permission and obligation. You may have heard auxiliary verbs referred to as helping verbs, but what is this type of verb, and what does it do in English?
When we say it is "helping" a main verb, we mean it's helping to clarify it. Explore what auxiliary verbs are and how they are used in English. You might have learned that auxiliary verbs are called "helping verbs." Modal verbs are a specific type of auxiliary verb.
They are used to denote permission, obligation, ability, or possibility. All of these modal verbs must come before a verb to help express at least one of the modality examples listed above. In some cases, though they can be used to express more than one modality, but you'll see more on that in the following section. So, let's take a look at some example sentences and highlight how the modal verb is expressing modality and adding more information to the verbs that follow them. We use modal verbs to express ability, to give advice, to ask for and give permission, to express obligation, to express possibility, to deduce and to make predicitions.
Modal verbs grammar can become especially confusing when taking a look at the verbs which follow the modal verb itself. Usually, modal verbs' grammar dictates that modal verbs are followed by the base form of the verb to the present or future moment. However, Modal verbs can also be used with other forms of verbs. The most common of these modal verbs' grammar forms is the use of the modal plus a perfect form to refer to a past time when using a modal verb of probability. Modal verbs are a part of the larger category called auxiliary verbs which are verbs that cannot be used on their own.
Sometimes modal verbs are called modal auxiliaries. Hawaiian Pidgin is a creole language most of whose vocabulary, but not grammar, is drawn from English. As is generally the case with creole languages, it is an isolating language and modality is typically indicated by the use of invariant pre-verbal auxiliaries.
The invariance of the modal auxiliaries to person, number, and tense makes them analogous to modal auxiliaries in English. However, as in most creoles the main verbs are also invariant; the auxiliaries are distinguished by their use in combination with a main verb. Today we fix any mistakes you might make with English modal verbs. With just 3 simple rules, you will eliminate the main issues you can think of when using these tricky verbs. If you have been having problems with learning English modal verb grammar , you must listen to this podcast. Modal verbs show intention, rather than action.
When used with other verbs in the sentence, they can make your meaning as clear as you want it to be. Test your knowledge of modal verbs with an examination of may vs. might. You can also make sure you're using can vs. could correctly in your writing and everyday speech. As a modal verb, "should" has many important uses in the English language. It's used to give advice, to express what's right, and to recommend an action. Also, it's used to make predictions, but ones that are more uncertain than those with the other modal verbs.
The modal verb "might" is used to express possibility in the present or in the future. It can be used as the verb "may" most times, however, it often means that the event has less possibility of happening than when it's said using may. Its negative form, "might not " is used to talk about possibilities but in a negative way.
It can be used to talk about ability and permission in the past. Also, just like the modal verb "can", the modal verb "could" can be used to make questions, requests, suggestions or offers, but in a more polite way. It can also be used to talk about possibilities, but not as strong possibility that the one expressed with "can". Since modal verbs are not the main verb in a sentence, they are not conjugated or inflected to show grammatical changes in the subject. They show ability, possibility, obligation, and permission. Examples of modal verbs are can, could, may, must, should, and would.
In definitions, it is referred to as a helping verb. There are certain modal verbs rules that encircle their use. It can be very beneficial if one can learn the rules and use of modal verbs as this will help you make grammatically correct English sentences. A modal verb is a type of verb that contextually indicates a modality such as a likelihood, ability, permission, request, capacity, suggestion, order, obligation, or advice. Modal verbs always accompany the base form of another verb having semantic content. In English, the modal verbs commonly used are can, could, may, might, shall, should, will, would, and must.
And do you have problems with modal verbs in English? If you do, you'll know that modal verbs appear all the time in English. So if you want to speak English without mistakes, you have to learn modal verbs.
How about today I give you three easy rules for modal verbs? And we'll do some practice at the end of the podcast. Nine of the ten English modal verbs are followed directly by the second verb, with no "to" in between. The main use of the modal verb "will" is to form the future form of the verbs in English.
When talking about demands and requests, the use of will sometimes is not as polite as other modal verbs. VerbTom and Suemightarrivelater.Everyonecanswim.In questions, the word order changes to modal + subject + main verb. Here are some examples with Yes / No questions.
These modal verbs are used to express different meanings of possibility and intention. They enhance the meanings of main verbs, and certain verbs are used to express each meaning. There are certain rules which surround the use of modal verbs, for example the word 'to' must never be used after a modal verb.
Learning these rules and how a modal verb can function within a sentence can greatly help you in forming grammatically correct sentences. Read the following examples and explanations carefully. In English grammar, a modal is a verb that combines with another verb to indicate mood or tense.
A modal, also known as a modal auxiliary or modal verb, expresses necessity, uncertainty, possibility, or permission. Modal verbs are used to express ability, obligation, permission, assumptions, probability and possibility, requests and offers, and advice. Each modal verb can have more than one meaning which depends on the context of that sentence . -,gamōtmaymögen, magmogen, magmögen, magmeie, meimagmå(må)mega, mámagum, magwissen, weißweten, weet?
Witte, witweetvedvetvita, veitwitum, wait(tharf)dürfen, darfdurven, durfdörven, dörvdoarre, doardurf? Þaúrbum, þarfThe English could is the preterite form of can; should is the preterite of shall; might is the preterite of may; and must was originally the preterite form of mote. (This is ignoring the use of "may" as a vestige of the subjunctive mood in English.) These verbs have acquired an independent, present tense meaning.
The German verb möchten is sometimes taught as a vocabulary word and included in the list of modal verbs, but it is actually the past subjunctive form of mögen. But notice that these do often get contracted - so 'She should not sing' becomes 'She shouldn't sing' and 'He could not speak French' becomes 'He couldn't speak French'. But we're just contracting here - showing how we shorten the words and join them together when we speak - it's really not changing the words or the word order much. 'We ought not to steal' becomes 'We oughtn't steal'. If you use 'ought' with 'not' it loses the 'to'.